Android - 多点触控
当超过一根手指同时触摸屏幕时,就会发生多点触控手势。 Android 允许我们检测这些手势。
当多个手指同时触摸屏幕时,Android 系统会生成以下触摸事件。
| 序号 | 事件 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
ACTION_DOWN 对于第一个接触屏幕的指针。 这将启动手势。 |
| 2 |
ACTION_POINTER_DOWN 对于超出第一个进入屏幕的额外指针。 |
| 3 |
ACTION_MOVE 在按下手势期间发生了变化。 |
| 4 |
ACTION_POINTER_UP 当非主指针上升时发送。 |
| 5 |
ACTION_UP 当最后一个指针离开屏幕时发送。 |
因此,为了检测上述任何事件,您需要重写 onTouchEvent() 方法并手动检查这些事件。 它的语法如下 −
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev){
final int actionPeformed = ev.getAction();
switch(actionPeformed){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:{
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:{
break;
}
return true;
}
}
在这些情况下,您可以执行任何您喜欢的计算。 例如缩放、缩小等。 为了得到 X 和 Y 轴的坐标,可以调用 getX() 和 getY() 方法。 它的语法如下 −
final float x = ev.getX(); final float y = ev.getY();
除了这些方法之外,这个 MotionEvent 类还提供了其他方法来更好地处理多点触控。 下面列出了这些方法 −
| 序号 | 方法 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
getAction() 此方法返回正在执行的操作类型 |
| 2 |
getPressure() 该方法返回该事件对第一个索引的当前压力 |
| 3 |
getRawX() 此方法返回此事件的原始原始 X 坐标 |
| 4 |
getRawY() 此方法返回此事件的原始原始 Y 坐标 |
| 5 |
getSize() 此方法返回第一个指针索引的大小 |
| 6 |
getSource() 该方法获取事件的来源 |
| 7 |
getXPrecision() 此方法返回被报告的 X 坐标的精度 |
| 8 |
getYPrecision() 此方法返回所报告的 Y 坐标的精度 |
示例
这是一个演示多点触控使用的示例。 它创建了一个基本的多点触控手势应用程序,允许您在执行多点触控时查看坐标。
要试验此示例,您需要在实际设备上运行它。
| 步骤 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 您将使用 android studio 在 com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication 包下创建一个 Android 应用程序。 |
| 2 | 修改 src/MainActivity.java 文件以添加多点触控代码。 |
| 3 | 修改 res/layout/activity_main 以添加相应的 XML 组件。 |
| 4 | 运行应用程序并选择一个正在运行的 android 设备并在其上安装应用程序并验证结果。 |
以下是修改后的主活动文件src/MainActivity.java的内容。
package com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
float xAxis = 0f;
float yAxis = 0f;
float lastXAxis = 0f;
float lastYAxis = 0f;
EditText ed1, ed2, ed3, ed4;
TextView tv1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ed1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
ed2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
ed3 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText3);
ed4 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText4);
tv1=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView2);
tv1.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
final int actionPeformed = event.getAction();
switch(actionPeformed){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:{
final float x = event.getX();
final float y = event.getY();
lastXAxis = x;
lastYAxis = y;
ed1.setText(Float.toString(lastXAxis));
ed2.setText(Float.toString(lastYAxis));
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:{
final float x = event.getX();
final float y = event.getY();
final float dx = x - lastXAxis;
final float dy = y - lastYAxis;
xAxis += dx;
yAxis += dy;
ed3.setText(Float.toString(xAxis));
ed4.setText(Float.toString(yAxis));
break;
}
}
return true;
}
});
}
}
以下是 res/layout/activity_main.xml 的修改内容。
在下面的代码中,abc表示 tutorialspoint.com 的标志
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:transitionGroup="true">
<TextView android:text="Multitouch example" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:textSize="35dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point"
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_below="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textColor="#ff7aff24"
android:textSize="35dp" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:theme="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textview"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textview"
android:hint="X-Axis"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textview"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/textview"
android:textColorHint="#ff69ff0e" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editText"
android:textColorHint="#ff21ff11"
android:hint="Y-Axis"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/editText" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editText2"
android:hint="Move X"
android:textColorHint="#ff33ff20"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/editText2" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText4"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editText3"
android:textColorHint="#ff31ff07"
android:hint="Move Y"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/editText3" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Touch here"
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/imageView"
android:focusable="true"
android:typeface="sans"
android:clickable="true"
android:textColor="#ff5480ff"
android:textSize="35dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
以下是 res/values/string.xml 的内容。
<resources> <string name="app_name">My Application</string> </resources>
以下是 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的内容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
让我们尝试运行您的应用程序。 我假设您已将实际的 Android 移动设备与您的计算机连接起来。 要从 Android Studio 运行应用程序,请打开项目的活动文件之一,然后单击工具栏中的 Run  图标。在启动您的应用程序之前,Android Studio 将显示以下窗口以选择您要运行 Android 应用程序的选项。
图标。在启动您的应用程序之前,Android Studio 将显示以下窗口以选择您要运行 Android 应用程序的选项。
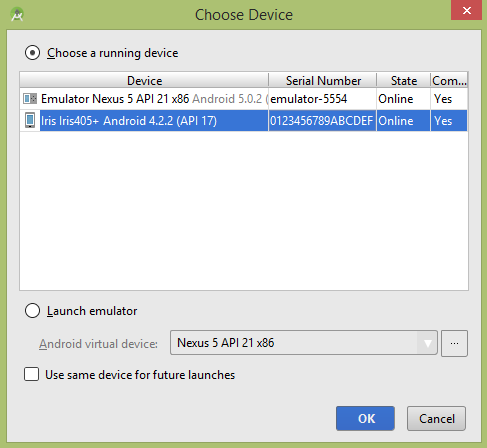
选择您的移动设备作为选项,然后检查您的移动设备,它将显示您的默认屏幕 −

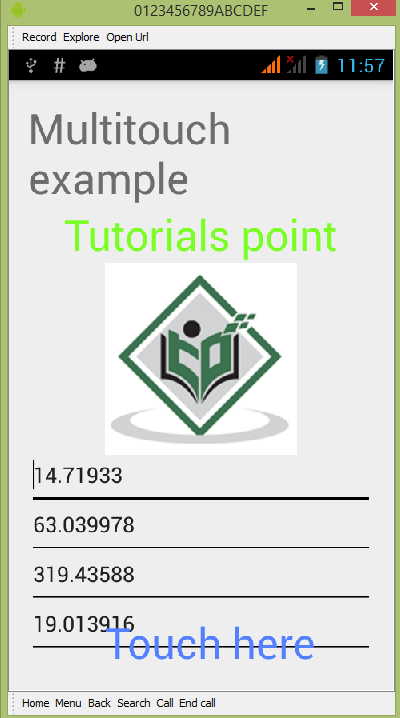
默认情况下,您不会在任何字段中看到任何内容。 现在只需点击触摸此处区域并查看字段中的一些数据。 如下图所示 −
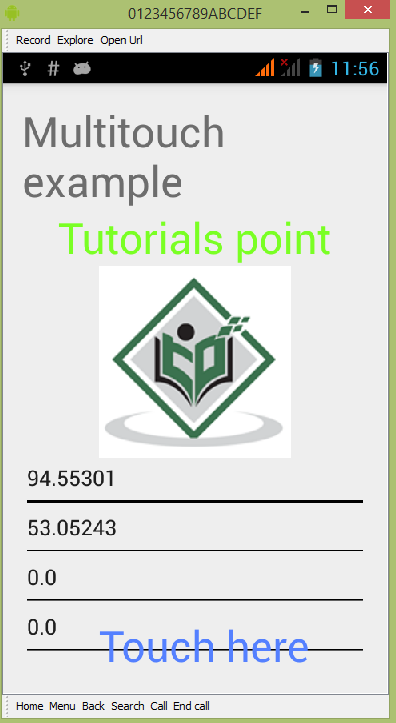
您将看到 Move 字段中的数据为 0,因为只执行了一个触摸手势。 现在点击屏幕并开始拖动手指。 您将看到移动字段数据的变化。 如下图所示 −