Electron - Hello World
我们已经为我们的项目创建了一个 package.json 文件。 现在我们将使用 Electron 创建我们的第一个桌面应用程序。
创建一个名为 main.js 的新文件。 在里面输入以下代码 −
const {app, BrowserWindow} = require('electron')
const url = require('url')
const path = require('path')
let win
function createWindow() {
win = new BrowserWindow({width: 800, height: 600})
win.loadURL(url.format ({
pathname: path.join(__dirname, 'index.html'),
protocol: 'file:',
slashes: true
}))
}
app.on('ready', createWindow)
创建另一个文件,这次是一个名为 index.html 的 HTML 文件。 在其中输入以下代码。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF-8">
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
We are using node <script>document.write(process.versions.node)</script>,
Chrome <script>document.write(process.versions.chrome)</script>,
and Electron <script>document.write(process.versions.electron)</script>.
</body>
</html>
使用以下命令运行此应用 −
$ electron ./main.js
将打开一个新窗口。 它将如下所示 −
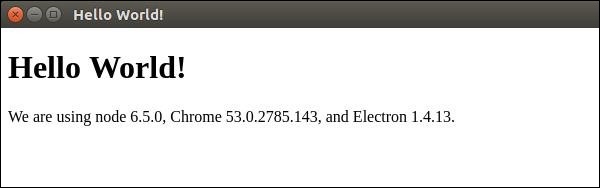
这个应用程序是如何工作的?
我们创建了一个主文件和一个 HTML 文件。 主文件使用两个模块 - app 和 BrowserWindow。 app 模块用于控制应用程序的事件生命周期,而 BrowserWindow 模块用于创建和控制浏览器窗口。
我们定义了一个 createWindow 函数,我们在其中创建一个新的 BrowserWindow 并将一个 URL 附加到这个 BrowserWindow。 这是我们运行应用程序时呈现并显示给我们的 HTML 文件。
我们在 html 文件中使用了原生 Electron 对象进程。 该对象从 Node.js 进程对象扩展而来,包括所有 t=its 功能,同时还添加了更多功能。


