Spring Cloud - 与 Feign 同步通信
简介
在分布式环境中,服务需要相互通信。 通信可以同步或异步发生。 在本节中,我们将了解服务如何通过同步 API 调用进行通信。
虽然这听起来很简单,但作为 API 调用的一部分,我们需要注意以下事项 −
Finding address of the callee − 调用者服务需要知道它要调用的服务的地址。
Load balancing − 调用者服务可以做一些智能的负载均衡,将负载分散到被调用者服务中。
Zone awareness − 调用者服务最好调用同一区域中的服务以快速响应。
Netflix Feign 和 Spring RestTemplate(以及 Ribbon)是用于进行同步 API 调用的两个著名的 HTTP 客户端。 在本教程中,我们将使用 Feign Client。
Feign - 依赖设置
让我们以我们在前几章中使用过的 Restaurant 为例。 让我们开发一个包含餐厅所有信息的餐厅服务。
首先,让我们使用以下依赖更新服务的 pom.xml −
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后,使用正确的注解来注解我们的 Spring 应用程序类,即 @EnableDiscoveryClient 和 @EnableFeignCLient
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class RestaurantService{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RestaurantService.class, args);
}
}
上述代码中的注意点 −
@ EnableDiscoveryClient − 这与我们用于读取/写入 Eureka 服务器的注解相同。
@EnableFeignCLient − 这个注解会在我们的代码中扫描我们的包以查找启用的 feign 客户端,并相应地对其进行初始化。
完成后,现在让我们简要介绍一下我们需要定义 Feign 客户端的 Feign 接口。
使用 Feign 接口进行 API 调用
可以通过在接口中定义 API 调用来简单地设置 Feign 客户端,该接口可以在 Feign 中用于构造调用 API 所需的样板代码。 例如,考虑我们有两个服务 −
服务 A − 使用 Feign 客户端的调用者服务。
服务 B − 上述 Feign 客户端调用其 API 的被调用者服务
调用者服务,即本例中的服务 A,需要为其打算调用的 API(即服务 B)创建一个接口。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "service-B")
public interface ServiceBInterface {
@RequestMapping("/objects/{id}", method=GET)
public ObjectOfServiceB getObjectById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@RequestMapping("/objects/", method=POST)
public void postInfo(ObjectOfServiceB b);
@RequestMapping("/objects/{id}", method=PUT)
public void postInfo((@PathVariable("id") Long id, ObjectOfBServiceB b);
}
注意事项 −
@FeignClient 注解了将由 Spring Feign 初始化的接口,并且可以被其余代码使用。
注意 FeignClient 注解需要包含服务的名称,这是用于发现服务地址,即来自 Eureka 或其他发现平台的服务 B。
然后我们可以定义我们计划从服务 A 调用的所有 API 函数名称。这可以是带有 GET、POST、PUT 等动词的一般 HTTP 调用。
完成后,服务 A 可以简单地使用以下代码调用服务 B 的 API −
@Autowired ServiceBInterface serviceB . . . ObjectOfServiceB object = serviceB. getObjectById(5);
让我们看一个例子,看看这个例子。
示例 - 使用 Eureka 的 Feign 客户端
假设我们要查找与客户所在城市位于同一城市的餐厅。 我们将使用以下服务 −
Customer Service − 拥有所有客户信息。 我们之前在 Eureka Client 部分已经定义了这一点。
Eureka Discovery Server − 有关于上述服务的信息。 我们之前在 Eureka Server 部分中已经定义了这一点。
Restaurant Service − 我们将定义的新服务包含所有餐厅信息。
让我们首先在我们的客户服务中添加一个基本控制器 −
@RestController
class RestaurantCustomerInstancesController {
static HashMap<Long, Customer> mockCustomerData = new HashMap();
static{
mockCustomerData.put(1L, new Customer(1, "Jane", "DC"));
mockCustomerData.put(2L, new Customer(2, "John", "SFO"));
mockCustomerData.put(3L, new Customer(3, "Kate", "NY"));
}
@RequestMapping("/customer/{id}")
public Customer getCustomerInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return mockCustomerData.get(id);
}
}
我们还将为上述控制器定义一个 Customer.java POJO。
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Customer {
private long id;
private String name;
private String city;
public Customer() {}
public Customer(long id, String name, String city) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.city = city;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
所以,一旦添加了这个,让我们重新编译我们的项目并执行以下查询开始 −
java -Dapp_port=8081 -jar .\target\spring-cloud-eureka-client-1.0.jar
注意 − 一旦启动了 Eureka 服务器和该服务,我们应该能够看到在 Eureka 中注册的该服务的实例。
要查看我们的 API 是否有效,让我们点击 http://localhost:8081/customer/1
我们将得到以下输出 −
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Jane",
"city": "DC"
}
这证明我们的服务运行良好。
现在让我们开始定义餐厅服务将用来获取客户城市的 Feign 客户端。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "customer-service")
public interface CustomerService {
@RequestMapping("/customer/{id}")
public Customer getCustomerById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
Feign 客户端包含服务的名称和我们计划在餐厅服务中使用的 API 调用。
最后,让我们在餐厅服务中定义一个使用上述接口的控制器。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
class RestaurantController {
@Autowired
CustomerService customerService;
static HashMap<Long, Restaurant> mockRestaurantData = new HashMap();
static{
mockRestaurantData.put(1L, new Restaurant(1, "Pandas", "DC"));
mockRestaurantData.put(2L, new Restaurant(2, "Indies", "SFO"));
mockRestaurantData.put(3L, new Restaurant(3, "Little Italy", "DC"));
}
@RequestMapping("/restaurant/customer/{id}")
public List<Restaurant> getRestaurantForCustomer(@PathVariable("id") Long
id) {
String customerCity = customerService.getCustomerById(id).getCity();
return mockRestaurantData.entrySet().stream().filter(
entry -> entry.getValue().getCity().equals(customerCity))
.map(entry -> entry.getValue())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
这里最重要的行如下 −
customerService.getCustomerById(id)
这就是我们之前定义的 Feign 客户端调用 API 的神奇之处。
让我们也定义 Restaurant POJO −
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Restaurant {
private long id;
private String name;
private String city;
public Restaurant(long id, String name, String city) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.city = city;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
定义好之后,让我们使用以下 application.properties 文件创建一个简单的 JAR 文件 −
spring:
application:
name: restaurant-service
server:
port: ${app_port}
eureka:
client:
serviceURL:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8900/eureka
现在让我们编译我们的项目并使用以下命令执行它 −
java -Dapp_port=8083 -jar .\target\spring-cloud-feign-client-1.0.jar
现在让我们编译我们的项目并使用以下命令执行它 −
Standalone Eureka 服务
Customer 服务
Restaurant 服务
我们可以通过 http://localhost:8900/ 上的仪表板确认上述内容正在运行
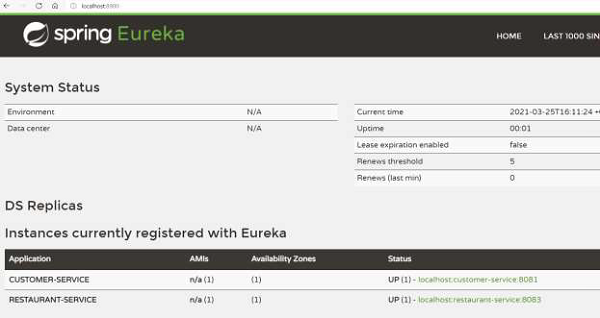
现在,让我们尝试找出所有可以为位于 DC 的 Jane 服务的餐厅。
For this, first let us hit the customer service for the same: http://localhost:8080/customer/1
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Jane",
"city": "DC"
}
And then, make a call to the Restaurant Service: http://localhost:8082/restaurant/customer/1
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Pandas",
"city": "DC"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Little Italy",
"city": "DC"
}
]
正如我们所看到的,Jane 可以在 DC 地区的 2 家餐厅提供服务。
另外,从客服的日志中,我们可以看到 −
2021-03-11 11:52:45.745 INFO 7644 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 1 ms Querying customer for id with: 1
总而言之,正如我们所见,无需编写任何样板代码甚至指定服务的地址,我们就可以对服务进行 HTTP 调用。
Feign 客户端 – 区域感知
Feign 客户端也支持区域感知。 比如说,我们收到一个服务的传入请求,我们需要选择应该为该请求提供服务的服务器。 与其在位于较远的服务器上发送和处理该请求,不如选择位于同一区域中的服务器更有成效。
现在让我们尝试设置一个区域感知的 Feign 客户端。 为此,我们将使用与前一个示例相同的情况。 我们将有以下 −
独立的 Eureka 服务器
区域感知客户服务的两个实例(代码与上面相同,我们将只使用"Eureka Zone Awareness"中提到的属性文件
区域感知餐厅服务的两个实例。
现在,让我们首先启动区域感知的客户服务。 回顾一下,这里是 application property 文件。
spring:
application:
name: customer-service
server:
port: ${app_port}
eureka:
instance:
metadataMap:
zone: ${zoneName}
client:
serviceURL:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8900/eureka
为了执行,我们将运行两个服务实例。 为此,让我们打开两个 shell,然后在一个 shell 上执行以下命令 −
java -Dapp_port=8080 -Dzone_name=USA -jar .\target\spring-cloud-eureka-client- 1.0.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:application-za.yml
并在另一个shell上执行以下 −
java -Dapp_port=8081 -Dzone_name=EU -jar .\target\spring-cloud-eureka-client- 1.0.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:application-za.yml
现在让我们创建区域感知的餐厅服务。 为此,我们将使用以下 application-za.yml
spring:
application:
name: restaurant-service
server:
port: ${app_port}
eureka:
instance:
metadataMap:
zone: ${zoneName}
client:
serviceURL:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8900/eureka
为了执行,我们将运行两个服务实例。 为此,让我们打开两个 shell,然后在一个 shell 上执行以下命令:
java -Dapp_port=8082 -Dzone_name=USA -jar .\target\spring-cloud-feign-client- 1.0.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:application-za.yml
并在另一个外壳上执行以下操作 −
java -Dapp_port=8083 -Dzone_name=EU -jar .\target\spring-cloud-feign-client- 1.0.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:application-za.yml
现在,我们已经在区域感知模式下设置了餐厅和客户服务的两个实例。
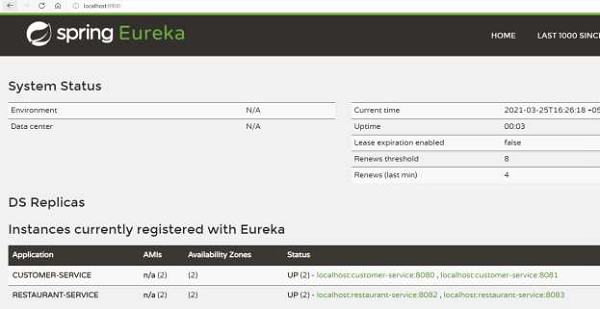
现在,让我们通过点击 http://localhost:8082/restaurant/customer/1 来测试这一点,我们正在点击 USA 区域。
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Pandas",
"city": "DC"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Little Italy",
"city": "DC"
}
]
但这里要注意的更重要的一点是,请求是由美国地区的客户服务提供的,而不是欧盟地区的服务。 例如,如果我们点击同一个 API 5 次,我们会看到运行在 USA 区域的客户服务在日志语句中会出现以下内容 −
2021-03-11 12:25:19.036 INFO 6500 --- [trap-executor-0] c.n.d.s.r.aws.ConfigClusterResolver : Resolving eureka endpoints via configuration Got request for customer with id: 1 Got request for customer with id: 1 Got request for customer with id: 1 Got request for customer with id: 1 Got request for customer with id: 1
而欧盟区的客户服务不提供任何请求。


