FastAPI - SQL 数据库
在上一章中,使用FastAPI 将Python 列表作为内存数据库来执行CRUD 操作。 相反,我们可以使用任何关系数据库(如 MySQL、Oracle 等)来执行存储、检索、更新和删除操作。
我们将使用 SQLAlchemy 作为 Python 代码和数据库之间的接口,而不是使用 DB-API 兼容的数据库驱动程序(我们将使用 SQLite 数据库,因为 Python 内置了对它的支持)。SQLAlchemy 是一种流行的 SQL 工具包和对象关系映射器。
对象关系映射是一种编程技术,用于在面向对象编程语言中的不兼容类型系统之间转换数据。 通常,像 Python 这样的面向对象语言中使用的类型系统包含非标量类型。 但是,Oracle、MySQL等数据库产品中的数据类型大多是整型、字符串等原始类型。
在 ORM 系统中,每个类都映射到底层数据库中的一个表。 无需自己编写繁琐的数据库接口代码,ORM 会为您处理这些问题,同时您可以专注于系统逻辑的编程。
为了使用 SQLAlchemy,我们需要先使用 PIP 安装程序安装库。
pip install sqlalchemy
SQLAlchemy 旨在使用为特定数据库构建的 DBAPI 实现进行操作。 它使用方言系统与各种类型的 DBAPI 实现和数据库进行通信。 所有方言都需要安装适当的 DBAPI 驱动程序。
以下是包含的方言 −
Firebird
Microsoft SQL Server
MySQL
Oracle
PostgreSQL
SQLite
Sybase
由于我们要使用 SQLite 数据库,我们需要为我们的数据库创建一个名为 test.db 的数据库引擎。 从 sqlalchemy 模块导入 create_engine() 函数。
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.dialects.sqlite import *
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL = "sqlite:///./test.db"
engine = create_engine(SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL, connect_args = {"check_same_thread": False})
为了与数据库进行交互,我们需要获取它的句柄。 会话对象是数据库的句柄。 会话类使用 sessionmaker() 定义 − 绑定到引擎对象的可配置会话工厂方法。
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, Session session = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
接下来,我们需要一个声明性基类,它在声明性系统中存储类目录和映射表。
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base Base = declarative_base()
Books 是 Base 的子类,映射到数据库中的 book 表。Books 类中的属性对应于目标表中列的数据类型。 请注意,id 属性对应于 book 表中的主键。
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String class Books(Base): __tablename__ = 'book' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, nullable=False) title = Column(String(50), unique=True) author = Column(String(50)) publisher = Column(String(50)) Base.metadata.create_all(bind=engine)
create_all() 方法在数据库中创建相应的表。
我们现在必须声明一个 Pydantic 模型,该模型对应于声明性基子类(上面定义的 Books 类)。
from typing import List
from pydantic import BaseModel, constr
class Book(BaseModel):
id: int
title: str
author:str
publisher: str
class Config:
orm_mode = True
注意在配置类中使用 orm_mode=True 表示它与 SQLAlchemy 的 ORM 类映射。
其余代码与内存CRUD操作类似,不同之处在于操作函数通过SQLalchemy接口与数据库交互。 FastAPI 应用程序对象上的 POST 操作定义如下 −
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends
app=FastAPI()
def get_db():
db = session()
try:
yield db
finally:
db.close()
@app.post('/add_new', response_model=Book)
def add_book(b1: Book, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
bk=Books(id=b1.id, title=b1.title, author=b1.author,
publisher=b1.publisher)
db.add(bk)
db.commit()
db.refresh(bk)
return Books(**b1.dict())
首先建立数据库会话。 来自 POST 请求正文的数据作为新行添加到 book 表中。 执行add_book()操作函数,将示例数据添加到books表中。 要进行验证,您可以使用 SQLiteStudio,它是 SQLite 数据库的 GUI 工具。
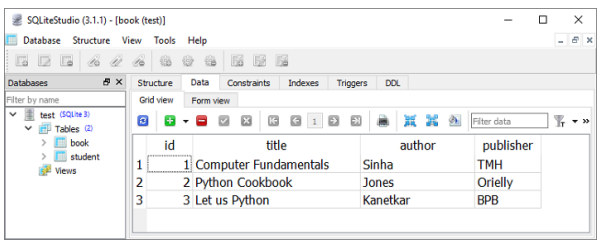
定义了两个GET操作的操作函数,一个是获取所有记录,一个是匹配某个路径参数的记录。
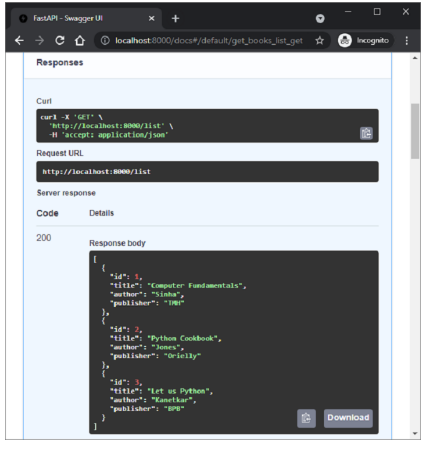
以下是绑定到 /list 路由的 get_books() 函数。 执行时,其服务器响应是所有记录的列表。
@app.get('/list', response_model=List[Book])
def get_books(db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
recs = db.query(Books).all()
return recs
/book/{id} 路由以 id 作为路径参数调用 get_book() 函数。 SQLAlchemy 的查询返回对应于给定 id 的对象。
@app.get('/book/{id}', response_model=Book)
def get_book(id:int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
return db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
下图显示了从 Swagger UI 执行的 get_books() 函数的结果。
更新和删除操作由 update_book() 函数(访问 /update/{id} 路由时执行)和 del_book() 函数执行,当路由 /delete/{id} 作为 URL 给出时调用。
@app.put('/update/{id}', response_model=Book)
def update_book(id:int, book:Book, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
b1 = db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
b1.id=book.id
b1.title=book.title
b1.author=book.author
b1.publisher=book.publisher
db.commit()
return db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
@app.delete('/delete/{id}')
def del_book(id:int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
try:
db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).delete()
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(e)
return {"delete status": "success"}
如果您打算使用任何其他数据库代替 SQLite,则只需相应地更改方言定义即可。 例如使用MySQL数据库和pymysql驱动,将engine对象的语句改成如下 −
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://user:password@localhost/test')


