Spring Security - JWT
内容
- JWT 简介和概述
- 使用 JWT 开始使用 Spring Security(实用指南)
JWT 简介和概述
JSON Web Token 或 JWT,因为它通常被称为,是一种开放的 Internet 标准 (RFC 7519),用于以紧凑的方式在各方之间安全地传输可信信息。令牌包含编码为 JSON 对象并使用私有密钥或公钥/私钥对进行数字签名的声明。它们是独立的且可验证的,因为它们经过了数字签名。 JWT 可以被签名和(或)加密。 签名的令牌验证令牌中包含的声明的完整性,而加密的令牌对其他方隐藏声明。
JWT 也可用于信息交换,尽管它们更常用于授权,因为与使用内存中随机令牌的会话管理相比,它们提供了很多优势。其中最大的一项是启用将身份验证逻辑委托给第三方服务器,如 AuthO 等。
JWT 令牌分为 3 部分,即标头、有效负载和签名,格式为
[Header].[Payload].[Signature]
Header − JWT 令牌的标头包含应用于 JWT 的列表加密操作。 这可以是签名技术、有关内容类型的元数据信息等。标头以 JSON 对象的形式呈现,该对象被编码为 base64URL。 有效 JWT 标头的示例是
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }
在这里,"alg"为我们提供了有关所用算法类型的信息,"typ" 为我们提供了信息的类型。
Payload − JWT 的有效负载部分包含要使用令牌传输的实际数据。 这部分也称为 JWT 令牌的"声明"部分。 索赔可以分为三种类型——注册的、公共的和私人的。
注册的声明是推荐的但不是强制性的声明,例如iss(issuer)、sub(subject)、aud(audience)等。
公共声明是由使用 JWT 的人定义的声明。
私人声明或自定义声明是为在相关方之间共享信息而创建的用户定义声明。
有效负载对象的示例可能是。
{ "sub": "12345", "name": "Johnny Hill", "admin": false }
有效负载对象(如标头对象)也是 base64Url 编码的,此字符串构成 JWT 的第二部分。
Signature− JWT 的签名部分用于验证消息在此过程中没有被更改。 如果令牌是用私钥签名的,它还会验证发件人是否就是它所说的那个人。它是使用编码的标头、编码的有效负载、秘密和标头中指定的算法创建的。 签名的一个例子是。
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret)
如果我们输入标头、有效负载和签名,我们会得到一个令牌,如下所示。
实例
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6I
kpvaG4gRG9lIiwiYWRtaW4iOmZhbHNlfQ.gWDlJdpCTIHVYKkJSfAVNUn0ZkAjMxskDDm-5Fhe
WJ7xXgW8k5CllcGk4C9qPrfa1GdqfBrbX_1x1E39JY8BYLobAfAg1fs_Ky8Z7U1oCl6HL63yJq_
wVNBHp49hWzg3-ERxkqiuTv0tIuDOasIdZ5FtBdtIP5LM9Oc1tsuMXQXCGR8GqGf1Hl2qv8MCyn
NZJuVdJKO_L3WGBJouaTpK1u2SEleVFGI2HFvrX_jS2ySzDxoO9KjbydK0LNv_zOI7kWv-gAmA
j-v0mHdJrLbxD7LcZJEGRScCSyITzo6Z59_jG_97oNLFgBKJbh12nvvPibHpUYWmZuHkoGvuy5RLUA
现在,可以在 Authorization 标头中使用此令牌,使用 Bearer 模式作为。
Authorization − Bearer <token>
使用 JWT 令牌进行授权是其最常见的应用。 令牌通常在服务器中生成并发送到客户端,并存储在会话存储或本地存储中。要访问受保护的资源,客户端将在上面给出的标头中发送 JWT。 我们将在下面的部分中看到 Spring Security 中的 JWT 实现。
使用 JWT 开始使用 Spring Security
我们将要开发的应用程序将使用 JWT 处理基本的用户身份验证和授权。 让我们从 start.spring.io 开始,我们将在其中创建一个具有以下依赖项的 Maven 应用程序。
- Spring Web
- Spring Security
我们生成项目,下载后,我们将其解压缩到我们选择的文件夹中。 然后我们可以使用我们选择的任何 IDE。 我将使用 Spring Tools Suite 4,因为它最适合 Spring 应用程序。
除了上述依赖项之外,我们还将包括来自 Maven 中央存储库的 io.jsonwebtoken 的 jwt 依赖项,因为它不包含在 spring 初始化程序中。此依赖项负责涉及 JWT 的所有操作,包括构建令牌、解析它以获取声明等。
实例
<dependency>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1</version>
</dependency>
我们的 pom.xml 文件现在应该与此类似。
实例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE<version>
<relativePath />
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.spring.security</groupId>
<artifactId>jwtbasic</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>jwtbasic</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test<scope>
<dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
现在我们的项目已经建立,我们将创建我们的控制器类 Hello Controller,它公开一个 Get 端点。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.controllers;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
现在我们将创建一个名为 config 的包,在其中添加扩展 Spring Security 的 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类的配置类。这将为我们提供项目配置和应用程序安全性所需的所有功能和定义。现在,我们通过实现一个生成该实例的方法来提供 BcryptPasswordEncoder 实例。 我们使用 @Bean 注解该方法以添加到我们的 Spring 上下文中。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.JwtFilter;
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
JWT 包含一个秘密,我们将在 application.properties 文件中定义它,如下所示。
secret=somerandomsecret
现在让我们创建一个名为 jwtutils 的包。 这个包将包含所有与 JWT 操作相关的类和接口,其中将包括。
- 生成令牌
- 验证令牌
- 检查签名
- 验证声明和权限
在这个包中,我们创建了第一个名为 Token Manager 的类。 此类将负责使用 io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts 创建和验证令牌。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims; import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
@Component
public class TokenManager implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7008375124389347049L; public static final long TOKEN_VALIDITY = 10 * 60 * 60; @Value("${secret}")
private String jwtSecret;
public String generateJwtToken(UserDetails userDetails) {
Map<String, Object> claims = new HashMap<>();
return Jwts.builder().setClaims(claims).setSubject(userDetails.getUsername())
.setIssuedAt(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()))
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + TOKEN_VALIDITY * 1000))
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, jwtSecret).compact();
}
public Boolean validateJwtToken(String token, UserDetails userDetails) {
String username = getUsernameFromToken(token);
Claims claims = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(jwtSecret).parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
Boolean isTokenExpired = claims.getExpiration().before(new Date());
return (username.equals(userDetails.getUsername()) && !isTokenExpired);
}
public String getUsernameFromToken(String token) {
final Claims claims = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(jwtSecret).parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
return claims.getSubject();
}
}
在这里,由于所有令牌都应该有一个到期日期,我们从一个令牌有效性常量开始。 在这里,我们希望我们的令牌在生成后 10 分钟内有效。我们将在生成令牌时使用此值。 然后我们使用 @Value 注解从 application.properties 文件中提取歌唱键的值到我们的 jwtSecret 字段中。
我们这里有两种方法 −
- generateJwtToken() − 此方法用于在用户成功验证时生成令牌。 要在此处创建令牌,我们使用用户名、令牌的发行日期和令牌的到期日期。这将形成我们之前讨论过的令牌或声明的有效负载部分。 要生成令牌,我们使用 Jwts 的 builder() 方法。 此方法返回一个新的 JwtBuilder 实例,该实例可用于创建紧凑的 JWT 序列化字符串。
要设置声明,我们使用 setClaims() 方法,然后设置每个声明。 对于这个令牌,我们设置了主题(用户名)、发行日期和到期日期。我们也可以像上面讨论的那样放置我们的自定义声明。 这可以是我们想要的任何值,可能包括用户角色、用户权限等。
然后我们设置令牌的签名部分。 这是使用 signWith() 方法完成的,我们设置了我们喜欢使用的散列算法和密钥。然后我们使用compact() 方法构建JWT 并根据JWT 紧凑序列化规则将其序列化为一个紧凑的、URL 安全的字符串。
validateJwtToken() − 现在已经处理了令牌的生成,当令牌作为请求的一部分出现时,我们应该关注令牌的验证过程。验证令牌意味着验证请求是经过身份验证的请求,并且令牌是生成并发送给用户的请求。 在这里,我们需要解析用户名、角色、权限、有效期等声明的令牌。
要验证令牌,我们需要先解析它。 这是使用 Jwts 的 parser() 方法完成的。然后,我们需要设置用于生成令牌的签名密钥,然后使用令牌上的 parseClaimsJws() 方法根据构建器的当前配置状态解析紧凑的序列化 JWS 字符串并返回生成的 Claims JWS 实例。然后使用 getBody() 方法返回在生成令牌时使用的声明实例。
从这个获得的声明实例中,我们提取主题和到期日期以验证令牌的有效性。用户名应该是用户的用户名,并且令牌不应过期。 如果这两个条件都满足,我们返回 true,这表示令牌是有效的。
我们将创建的下一个类是 JwtUserDetailsService。 此类将扩展 Spring 安全性的 UserDetailsService,我们将实现 loadUserByUsername() 方法,如下所示 −
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class JwtUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
if ("randomuser123".equals(username)) {
return new User("randomuser123",
"$2a$10$slYQmyNdGzTn7ZLBXBChFOC9f6kFjAqPhccnP6DxlWXx2lPk1C3G6",
new ArrayList<>());
} else {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found with username: " + username);
}
}
}
在这里,由于这是一个仅用于演示 JWT 身份验证的基本应用程序,因此我们使用了一组用户详细信息,而不是使用数据库。为了方便起见,我们将用户名设为"randomuser123"并将密码"password"编码为"$2a$10$slYQmyNdGzTn7ZLBXBChFOC9f6kFjAqPhccnP6DxlWXx2lPk1C3G6"。
接下来,我们为请求和响应模型创建类。 这些模型决定了我们的请求和响应格式将如何进行身份验证。下面给出的第一个快照是请求模型。 正如我们所看到的,我们将在我们的请求中接受两个属性——用户名和密码。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.models;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class JwtRequestModel implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2636936156391265891L;
private String username;
private String password;
public JwtRequestModel() {
}
public JwtRequestModel(String username, String password) {
super();
this.username = username; this.password = password;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
下面是成功认证的响应模型代码。 如我们所见,我们将在成功验证后将令牌发送回用户。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.models;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class JwtResponseModel implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String token;
public JwtResponseModel(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
}
对于现在的身份验证,让我们创建一个控制器,如下所示。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.DisabledException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.models.JwtRequestModel;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.models.JwtResponseModel;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class JwtController {
@Autowired
private JwtUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private TokenManager tokenManager;
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseEntity<> createToken(@RequestBody JwtRequestModel
request) throws Exception {
try {
authenticationManager.authenticate(
new
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(request.getUsername(),
request.getPassword())
);
} catch (DisabledException e) {
throw new Exception("USER_DISABLED", e);
} catch (BadCredentialsException e) {
throw new Exception("INVALID_CREDENTIALS", e);
}
final UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(request.getUsername());
final String jwtToken = tokenManager.generateJwtToken(userDetails);
return ResponseEntity.ok(new JwtResponseModel(jwtToken));
}
}
如果我们通过代码可以看到,我们已经自动装配了三个依赖项,即 JwtUserDetailsService、AuthenticationManager 和 TokenManager。虽然我们已经在上面看到了 JwtUserDetailsService 和 TokenManager 类的实现,但身份验证管理器 bean 是我们将在 WebSecurityConfig 类中创建的一个。
AuthenticationManager 类将负责我们的身份验证。 我们将使用 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 模型来验证请求。如果身份验证成功,我们将为用户生成一个 JWT,该 JWT 可以在后续请求的 Authorization 标头中发送以获取任何资源。
正如我们所见,我们正在使用 JwtUserDetailsService 类的 loadUserByUsername() 方法和 TokenManager 中的 generateJwtToken() b> 类。
如上所述,此生成的 JWT 作为对成功身份验证的响应发送给用户。
现在是我们创建过滤器的时候了。 过滤器类将用于跟踪我们的请求并检测它们是否在标头中包含有效令牌。 如果令牌有效,我们让请求继续,否则我们发送 401 错误 (Unauthorized)。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetailsSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import io.jsonwebtoken.ExpiredJwtException;
@Component
public class JwtFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private JwtUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private TokenManager tokenManager;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String tokenHeader = request.getHeader("Authorization");
String username = null;
String token = null;
if (tokenHeader != null && tokenHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
token = tokenHeader.substring(7);
try {
username = tokenManager.getUsernameFromToken(token);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("Unable to get JWT Token");
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
System.out.println("JWT Token has expired");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Bearer String not found in token");
}
if (null != username &&SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if (tokenManager.validateJwtToken(token, userDetails)) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
userDetails, null,
userDetails.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(new
WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
正如我们在上面看到的,我们在这里也自动装配了 JwtUserDetailsService 和 TokenManager 类。我们扩展了 SpringSecurity 的 OncePerRequestFilter ,确保每个请求都运行过滤器。 我们已经为 OncePerRequestFilter 类的重写方法 doFilterInternal() 提供了我们的实现。
这里的方法从标头中提取令牌并在我们的 TokenManager 类的 validateJwtToken() 方法的帮助下对其进行验证。在验证期间,它会检查用户名和到期日期。 如果两个值都有效,我们将身份验证保存在 Spring Security 上下文中,并让代码继续执行过滤器链中的下一个过滤器。如果任何验证失败或令牌存在问题或找不到令牌,我们将抛出适当的异常并发送回适当的响应,同时阻止请求继续进行。
为我们的请求创建过滤器后,我们现在创建 JwtAutheticationEntryPoint 类。这个类扩展了 Spring 的 AuthenticationEntryPoint 类,并拒绝每个未经身份验证的请求,并将错误代码 401 发送回客户端。 我们已经重写了 AuthenticationEntryPoint 类的 begin() 方法来做到这一点。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint,
Serializable {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws
IOException, ServletException {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED,
"Unauthorized");
}
}
现在,让我们回到我们的 WebSecurityConfig 类并完成剩下的配置。如果我们记得,我们将为 Jwt 控制器类需要我们的 AuthenticationManager bean,并将我们刚刚创建的过滤器添加到我们的配置中。我们还将配置哪些请求要经过身份验证,哪些不需要。我们还将 AuthenticationEntryPoint 添加到我们的请求中以发送回 401 错误响应。因为,我们也不需要在使用 jwt 时维护会话变量,我们可以使我们的会话 STATELESS 无状态。
实例
package com.spring.security.jwtbasic.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import com.spring.security.jwtbasic.jwtutils.JwtFilter;
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private JwtFilter filter;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws
Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint)
.and()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
http.addFilterBefore(filter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
正如我们所看到的,我们已经完成了所有这些,现在我们的应用程序已经准备就绪。 让我们启动应用程序并使用 postman 来发出我们的请求。
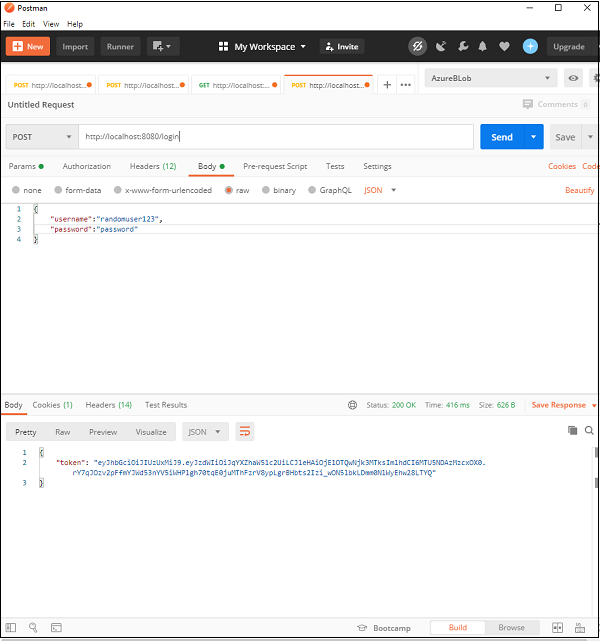
在这里,我们发出了第一个获取令牌的请求,正如我们在提供正确的用户名/密码组合时看到的那样,我们取回了我们的令牌。
现在在我们的标头中使用该令牌,让我们调用 /hello 端点。
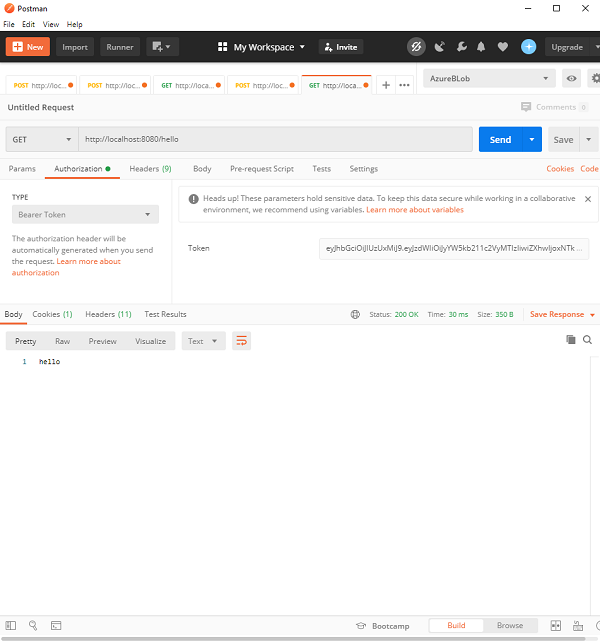
正如我们所看到的,由于请求已通过身份验证,我们得到了所需的响应。 现在,如果我们篡改令牌或不发送授权标头,我们将收到应用程序中配置的 401 错误。 这确保了使用 JWT 保护我们的请求。


