Python 设计模式 - 面向对象的概念实现
在本章中,我们将重点介绍使用面向对象概念的模式及其在 Python 中的实现。 当我们围绕语句块设计程序时,这些语句块围绕函数操作数据,这称为面向过程的编程。 在面向对象的编程中,有两个主要的实例,称为类和对象。
Python 如何实现类和对象变量?
类和对象变量的实现如下 −
class Robot:
population = 0
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
print("(Initializing {})".format(self.name))
Robot.population += 1
def die(self):
print("{} is being destroyed!".format(self.name))
Robot.population -= 1
if Robot.population == 0:
print("{} was the last one.".format(self.name))
else:
print("There are still {:d} robots working.".format(
Robot.population))
def say_hi(self):
print("Greetings, my masters call me {}.".format(self.name))
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
print("We have {:d} robots.".format(cls.population))
droid1 = Robot("R2-D2")
droid1.say_hi()
Robot.how_many()
droid2 = Robot("C-3PO")
droid2.say_hi()
Robot.how_many()
print("\nRobots can do some work here.\n")
print("Robots have finished their work. So let's destroy them.")
droid1.die()
droid2.die()
Robot.how_many()
输出
以上程序生成如下输出 −
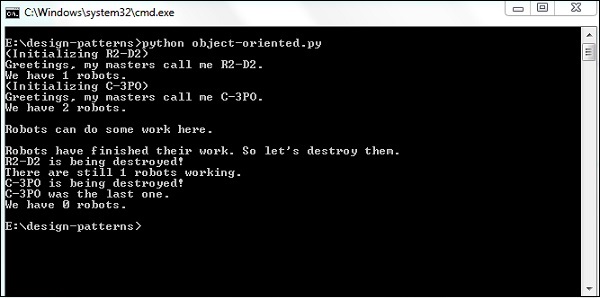
说明
此图有助于展示类和对象变量的性质。
"population"属于"Robot"类。 因此,它被称为类变量或对象。
在这里,我们将 population 类变量称为 Robot.population 而不是 self.population。


