PL/SQL - IF-THEN 语句
它是IF控制语句的最简单形式,经常用于决策和改变程序执行的控制流。
IF 语句 将条件与关键字THEN 和END IF 包围的语句序列相关联。如果条件为 TRUE,则执行语句,如果条件为 FALSE 或 NULL,则 IF 语句什么都不做。
语法
IF-THEN 语句的语法是 −
IF condition THEN S; END IF;
其中 condition 是布尔或关系条件,而 S 是简单或复合语句。 以下是 IF-THEN 语句的示例 −
IF (a <= 20) THEN c:= c+1; END IF;
如果布尔表达式条件的计算结果为真,则 if 语句 中的代码块将被执行。如果布尔表达式的计算结果为假,则将执行 if 语句 结束之后(结束 if 之后)的第一组代码。
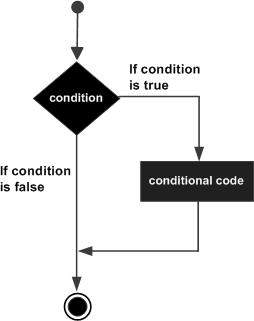
流程图
示例 1
让我们尝试一个可以帮助您理解概念的示例 −
DECLARE
a number(2) := 10;
BEGIN
a:= 10;
-- check the boolean condition using if statement
IF( a < 20 ) THEN
-- if condition is true then print the following
dbms_output.put_line('a is less than 20 ' );
END IF;
dbms_output.put_line('value of a is : ' || a);
END;
/
在 SQL 提示符下执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 −
a is less than 20 value of a is : 10 PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
示例 2
考虑我们在 PL/SQL 变量类型中创建的表和表中的少量记录
DECLARE
c_id customers.id%type := 1;
c_sal customers.salary%type;
BEGIN
SELECT salary
INTO c_sal
FROM customers
WHERE id = c_id;
IF (c_sal <= 2000) THEN
UPDATE customers
SET salary = salary + 1000
WHERE id = c_id;
dbms_output.put_line ('Salary updated');
END IF;
END;
/
在 SQL 提示符下执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 −
Salary updated PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.


