在 express.js 中处理不同的路由
node.jsserver side programmingprogramming更新于 2025/4/15 0:52:17
要处理不同的路由,请使用 use() 函数。 use() 函数有多个重载版本,其中一个版本还将 url 路径作为参数。 根据 url 路径,将针对相应的中间件过滤出请求。
const http = require('http');
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use('/', (req, res,next)=>{
console.log('first middleware');
res.send('<h1> first midleware:
Hello Tutorials Point </h1>');
});
const server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000);
在上面的例子中,我们使用‘/’作为 url 路径,这是默认的。
现在,由于每个路由都以‘/’开头,上面的中间件会针对每个 http 请求执行。它适用于‘/’和‘/username’。
为了避免上述问题,我们必须先使用路径特定的中间件,然后再使用默认中间件。
const http = require('http');
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use('/username', (req, res,next)=>{
res.send('<h1> My username </h1>');
});
app.use('/', (req, res,next)=>{
console.log('first middleware');
res.send('<h1> first midleware: Hello Tutorials Point </h1>');
});
const server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000);
现在,我们使用‘/username’ path 中间件首先,因为我们没有在其中使用 next() ,所以它不会将 http 请求传递给下一个中间件。
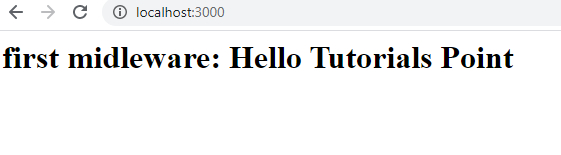
因此,我们看到浏览器对不同的 url 输出如下 −
localhost:3000
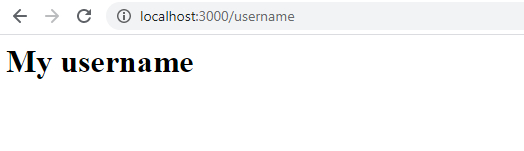
对于 localhost:3000/username
如果对 http 请求的任何预处理都需要,则使用默认中间件 URL 路径 ‘/’ 很有用。我们只需要在其中使用 next() 将预处理后的请求传递给下一个中间件即可。
const http = require('http');
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use('/', (req, res,next)=>{
console.log('log request info', req);
next();
});
app.use('/username', (req, res,next)=>{
res.send('<h1> My username </h1>');
});
app.use('/', (req, res,next)=>{
console.log('first middleware');
res.send('<h1> first midleware: Hello Tutorials Point </h1>');
});
const server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000);

