C++ 中的二叉树垂直顺序遍历
c++server side programmingprogramming更新于 2024/8/30 16:19:00
假设有一棵二叉树,我们必须找到其节点值的垂直顺序遍历。如果两个节点位于同一行和列,则顺序应从左到右。
因此,如果输入如下,
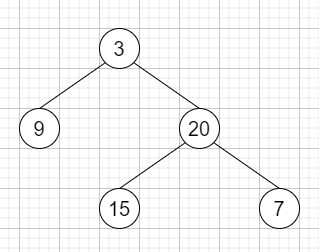
则输出将是 [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
为了解决这个问题,我们将遵循以下步骤 −
定义一个映射 m
定义一个函数 resolve(),它将获取节点 x,并将其初始化为 0,
如果节点为空,则 −
返回
solve(节点左侧,x - 1)
solve(节点右侧,x + 1)
在 m[x] 末尾插入节点值
从主方法中,执行以下操作 −
如果 root 为 null,则 −
返回 {
定义一个队列 q
将 { 0, root } 插入 q
在 m[0] 末尾插入节点值
当(q 不为空)时,执行−
sz := q 的大小
当 sz 非零时,在每次迭代中减少 sz,执行 −
curr := q 的第一个元素
从 q 中删除元素
node = curr 的第二个元素
x := curr 的第一个元素
如果节点的左侧不为空,则 −
将 { x - 1, 节点的左侧} 插入 q
节点的左侧位于 m[x - 1] 的末尾
如果右侧节点不为空,则 −
将 { x - 1, 节点右侧} 插入 q
节点右侧位于 m[x - 1] 的末尾
定义一个二维数组 ret
对 m 中的每个键值对 'it' 执行 −
将其值插入 ret 中
return ret
示例
让我们看下面的实现,以便更好地理解 −
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void print_vector(vector<vector<auto< > v){
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i<v.size(); i++){
cout << "[";
for(int j = 0; j <v[i].size(); j++){
cout << v[i][j] << ", ";
}
cout << "],";
}
cout << "]"<<endl;
}
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}
else{
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}
else{
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int< v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
class Solution {
public:
map<int, vector<int< > m;
void solve(TreeNode* node, int x = 0){
if (!node || node->val == 0)
return;
solve(node->left, x - 1);
solve(node->right, x + 1);
m[x].push_back(node->val);
}
static bool cmp(vector<int<& a, vector<int<& b){
return a[0] != b[0] ? a[0] < b[0] : a[1] < b[1];
}
vector<vector<int< > verticalOrder(TreeNode* root){
if (!root)
return {};
queue<pair > q;
q.push({ 0, root });
m[0].push_back(root->val);
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
while (sz--) {
pair<int, TreeNode*> curr = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode* node = curr.second;
int x = curr.first;
if (node->left && node->left->val != 0) {
q.push({ x - 1, node->left });
m[x - 1].push_back(node->left->val);
}
if (node->right && node->right->val != 0) {
q.push({ x + 1, node->right });
m[x + 1].push_back(node->right->val);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int< > ret;
map<int, vector<int< >::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end()) {
ret.push_back(it->second);
it++;
}
return ret;
}
};
main(){
Solution ob;
vector<int< v = {3,9,20,NULL,NULL,15,7};
TreeNode *root = make_tree(v);
print_vector(ob.verticalOrder(root));
}
输入
{3,9,20,NULL,NULL,15,7}
输出
[[9, ],[3, 15, ],[20, ],[7, ],]

